Car Insurance 2023 : How to find low-cost car insurance in Canada!
There can be a BIG difference between auto insurance premiums for motorists living in different provinces. In Québec, for instance, where average car insurance is the cheapest, rates cost about 165% lower than those in British Columbia, where premiums are priced the highest.
There are several strategies you can use to save money on your car insurance costs without sacrificing coverage or protection. Insurance Business has referred to the websites of various industry specialists, from personal finance firms to auto insurers, for practical tips. Here are some of the strategies we gathered:
1. Review your policy annually to determine how much coverage you actually need.
It’s easy to sign up for a car insurance policy and forget about it, but it’s important to review your coverage periodically. You might be paying for more coverage than you really need, or you might be able to save money by adjusting your policy. Take the time to review your policy and make changes as needed.
2. Consider usage-based insurance or telematics.
Usage-based insurance, also known as pay-per-mile insurance, charges you based on how much you drive. Telematics, on the other hand, tracks your driving habits to provide personalized rates. Both options can be a good choice if you don’t drive very much or if you’re a safe driver.
3. Maintain a good credit history.
Your credit score can have an impact on your car insurance rates. Maintaining a good credit history can help you get lower rates. Make sure to pay your bills on time and keep your credit utilization low.
4. Install safety features in your vehicle.
Safety features such as an upgraded alarm system or snow tires during winter can help you qualify for discounts on your car insurance. These features can also help keep you safe on the road.
5. Keep a clean driving record.
A clean driving record is one of the best ways to keep your car insurance rates low. Avoid accidents and traffic violations to keep your record clean.
6. Choose vehicles that have excellent crash test ratings, low-theft scores, and are not sporty or attract lots of attention.
The type of car you drive can also impact your car insurance rates. Choose vehicles that have excellent crash test ratings and low-theft scores to help keep your rates low. Avoid sporty cars or vehicles that attract lots of attention.
7. Bundle policies together.
Bundling your car insurance with other types of insurance, such as homeowners’ or renters insurance, can help you save money on both policies. Many insurance companies offer discounts for bundling.
8. Consider a higher deductible.
A higher deductible can help you save money on your car insurance premiums. Just make sure you have enough money set aside to cover the deductible in case of an accident.
9. Shop around for and compare rates.
Don’t be afraid to shop around for car insurance. Compare rates from several different insurers to find the best deal. Make sure you’re comparing apples to apples by looking at the same coverage levels and deductibles.
10. Never miss a payment.
Missing a car insurance payment can result in late fees and a lapse in coverage. Make sure to pay your premiums on time to avoid these extra costs.
Insurance Business examined quotes from various price comparison websites to get a sense of how much auto insurance premiums cost across the nation. Several big auto insurers’ quotes were also examined. The amount that drivers pay in premiums each year in each province and territory is shown in the table below, starting with the cheapest auto insurance in Canada.
It’s important to keep in mind that the numbers below are only estimates and that actual costs will change based on each driver’s unique needs.
pic credits: Insurance Business
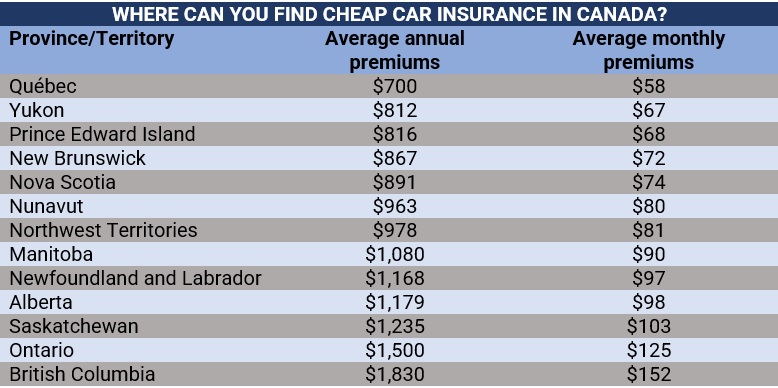
Here are some of the parameters that car insurance companies consider when determining your auto insurance rates:
- Age: Your age is one of the most significant factors that can influence your auto insurance rates. Younger drivers are statistically more likely to get into accidents, and as a result, they tend to pay higher insurance premiums. Drivers over the age of 25 generally see a decrease in their insurance rates, as they are considered more experienced and less risky drivers.
- Gender: Men are statistically more likely to get into accidents than women, and this is reflected in their insurance premiums. Male drivers usually pay higher premiums than female drivers, although this gap is starting to close in some countries.
- Postal code: Where you live can also affect your insurance rates. Drivers who live in areas with higher rates of car theft, vandalism, and accidents generally pay more for their insurance. Conversely, drivers who live in safer neighborhoods with lower crime rates and fewer accidents can often get cheaper insurance rates.
- Driving record: Your driving record is a critical factor that determines your auto insurance rates. Drivers with a clean driving record and no history of accidents or traffic violations are considered low-risk drivers and are rewarded with lower insurance premiums. On the other hand, drivers with a history of accidents or violations will likely have to pay higher rates.
- Mileage: The number of miles you drive annually can also affect your insurance rates. Drivers who drive more miles are more likely to get into accidents than those who drive less, and as a result, they tend to pay higher insurance premiums.
Operating a vehicle in Canada comes with a major responsibility, and that is to carry auto insurance. It is mandatory to have car insurance in all provinces and territories. Driving without an insurance policy can lead to hefty fines and even affect your eligibility to obtain coverage in the future. However, there is a significant difference in how the car insurance system works between provinces and territories.Let’s take a closer look at the different auto insurance systems across Canada.
For those who reside in British Columbia and Manitoba, auto insurance is regulated by government-owned organizations, the Insurance Corporation of British Columbia (ICBC), and Manitoba Public Insurance (MPI). Both ICBC and MPI offer basic coverage that includes third-party liability, accident benefits, and uninsured automobile coverage. However, British Columbia and Manitoba have different systems for determining fault in an accident. In British Columbia, fault is allocated based on a percentage system, while Manitoba follows a “no-fault” system, where each driver’s insurance covers their own damages.
In Saskatchewan, car insurance is also run by a crown corporation, Saskatchewan Government Insurance (SGI). However, motorists can purchase additional coverage through private insurers. SGI offers a basic package that includes liability, collision, and comprehensive coverage. Additionally, drivers can add on extra coverage such as loss of use, extra liability, or a deductible waiver.
Québec has a unique system for car insurance. The Société de l’assurance Automobile du Québec (SAAQ), another public institution, handles minimum limits for bodily injury, while private companies offer third-party liability, property damage, and additional protection. The SAAQ offers a basic package that covers bodily injury, while private insurers offer additional coverage such as collision, comprehensive, and third-party liability.
In Ontario, car insurance is regulated by the Financial Services Regulatory Authority of Ontario (FSRA). Ontario has a no-fault insurance system, meaning that each driver’s insurance company covers their own damages regardless of who is at fault. Basic coverage includes third-party liability, accident benefits, and uninsured automobile coverage. However, drivers can purchase additional coverage, such as collision, comprehensive, and increased liability if they wish.
In Atlantic Canada, auto insurance is regulated by each province’s insurance board. For example, in Nova Scotia, the Nova Scotia Utility and Review Board regulates automobile insurance. Basic coverage includes third-party liability and accident benefits, while optional coverage includes collision, comprehensive, and increased liability.
The table below sums up the mandatory coverages in each Canadian province and territory.
pic credits: Insurance Business
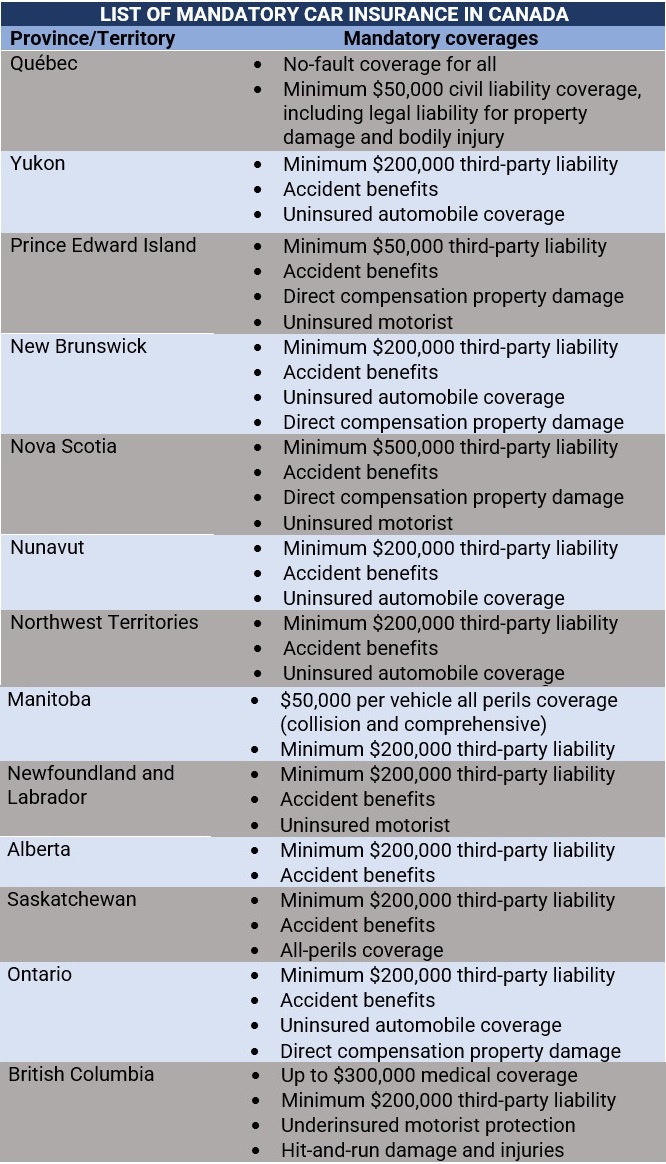
it is essential to have auto insurance when operating a vehicle in Canada. Each province and territory has its own insurance system, and it is crucial to understand the differences in coverage and regulations. No matter where you reside in Canada, make sure to research and obtain car insurance to protect yourself and others on the road.



